What is a DDoS Attack?
A distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attack is one in which multiple compromised computer systems attack a target and cause a denial of service for users of the targeted resource. This target could refer to a website, server, or several other network resources. The flood of connection requests, incoming messages, or malformed packets to the target system forces it to slow down or even crash and shut down, thus denying service to genuine users or systems.
When compared to other forms of cyberattacks, DDoS attacks offer a less complex attack mode, but they are growing, even more, stronger and are becoming increasingly sophisticated. Three basic categories of DDoS attacks include:
- Protocol attacks: Focus on exploiting server resources
- Volume-based attacks: High traffic is used to flood the network bandwidth
- Application attacks: Target web applications and are treated to be the most refined and serious type of attacks.
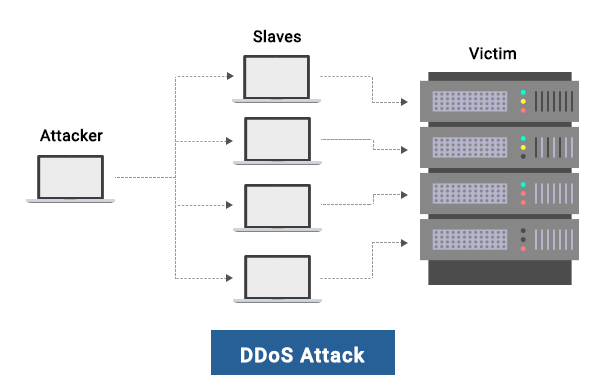
How DDoS Attacks Work?
In any typical DDoS attack, the assailant starts by exploiting a vulnerability in one computer system and then makes it the DDoS master. The attack master system detects other vulnerable systems and gets control over them by either contaminating the systems with malware or bypassing the authentication controls (in other words, guessing the default password on an extensively used device or system).
A networked device or computer under the control of an intruder is called a bot or zombie. The attacker develops a command-and-control server to command the network of bots, also known as a botnet. Sometimes. the person in control of a botnet is referred to as the botmaster. Botnets can contain any number of bots. Botnets with tens or hundreds of thousands of nodes have gained immense popularity, and there may not be an upper limit to their size. After the botnet gets assembled, the attacker will be able to use the traffic generated by the compromised devices in order to flood the target domain and knock it offline.
The goal of a DDoS attack is either to block legitimate users from accessing services and cause costly downtime. Some of the reasons why an individual could issue a DDoS attack include:
- Revenge
- Politics
- Extortion
- Competition
- Pranks
- Random attacks
- Cloaking other criminal activity (data theft)
- Hackers interested in establishing a reputation
- Tests by governments or hackers
DDoS Mitigation
The very first line of defense for an effective DDoS protection strategy includes an existing firewall, load balancers, and intrusion prevention system (IPS). Furthermore, dedicated DDoS protection devices are also capable of providing specialized mitigation against advanced and large-scale DDoS attacks. These DDoS protection devices will have to provide sufficient headroom in terms of throughput, bandwidth, and connectivity to handle DDoS attacks while maintaining service availability.
With DDoS protection devices integrating with a wide range of solutions from different vendors, it is important that these solutions can adjust to changing needs and integrate effortlessly through common APIs.
cWatch: A DDoS Protection Tool
Even though DDoS prevention can be executed via manual security planning, it could indeed be a lot easier if you have your own DDoS prevention tool. Having your own tool is essential because DDoS attacks can happen anytime, and you need to be readily equipped to handle these attacks and also prevent them.
As a DDoS protection tool, cWatch is a reliable web security solution offering the most efficient features for any business. This tool combines a Web Application Firewall (WAF) provisioned over a Secure Content Delivery Network (CDN). Web security is taken care of 24/7 by a Cyber Security Operation Center (CSOC) of certified security analysts. This tool is powered by a Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) capable of leveraging data from more than 85 million endpoints to identify and mitigate threats even before they occur.
The cWatch DDoS Protection Tool offers the following key features:
- Web Application Firewall (WAF)
The Comodo WAF offers powerful, real-time edge protection for websites and web applications providing advanced security, filtering, and intrusion protection. This WAF eliminates application vulnerabilities and provides protection against advanced attacks that include DDoS, Cross-Site Scripting, and SQL Injection. - Malware Monitoring and Remediation
As a DDoS protection tool, cWatch detects malware, provides the methods and tools to remove it, and prevents future malware attacks. - Cyber Security Operations Center (CSOC)
The CSOC has a team of always-on certified cybersecurity professionals providing round-the-clock surveillance and remediation services. - Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)
Enhanced intelligence leveraging current events and data from 85M+ endpoints and 100M+ domains. - PCI Scanning
This scanning enables service providers and merchants to stay in compliance with the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS). - Secure Content Delivery Network (CDN)
A global system of distributed servers to enhance the performance of web applications and websites.
Related Resources
How to Protect against DDoS Attack





