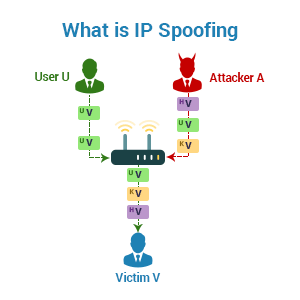
What is IP Address Spoofing?
IP address spoofing refers to a computer hacking technique that sends IP packets using an IP source that has not been assigned to the computer which sends them. This technique is mostly used by hackers to launch man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks and distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks against targeted devices or the surrounding infrastructures.
Using spoofed IP addresses can allow hackers to:
- Prevent targeted devices from sending alerts about attacks in which they are unwitting and unwilling participants
- Avoid being discovered and implicated by the authorities as well as forensic cyber investigators
- Bypass security scripts, services, and devices that try to mitigate DDoS attacks by blacklisting IP addresses known to be sources of malicious traffic.
Types of Attacks Implemented through IP Spoofing
The following attacks can be caused by the IP spoofing:
-
Denial-of-Service Attack
In a DoS attack, hackers focus on consuming bandwidth and resources by flooding the target host machine with as many packets as possible within a short time period. Hackers spoof source IP addresses to complicate the tracing and stopping attempts of the DDoS. The attacker scans the internet, detects the hosts with known vulnerabilities, compromises them to install the attack program, and finally exploits the vulnerabilities to gain the root access.
-
Man-in-the-Middle-Attack
When two machines communicate with each other, the hacker interrupts the packets sent by the systems and changes the packets with the sending and receiving machines just not aware that their communication has been tampered.
-
Blind Spoofing
Attackers transmit multiple packets to their intended target in order to receive a series of numbers which are usually used to assemble packets in the order in which they intend to read the packets. In a blind spoofing attack, hackers are totally not aware of how the transmissions take place on this network and hence they need to coax the machine into responding to their requests allowing them to examine the sequence numbers. Now, the attackers will be able to inject data into the stream of packets without authenticating themselves when the connection was initially established.
-
Non-Blind Spoofing
This type of attack occurs when the hacker is on the same subnet as the target that can see sequence and acknowledgement of every single packet. This type of spoofing attack is session hijacking and an attacker will be able to bypass any authentication measures taken to build the connection. This is accomplished by corrupting the DataStream of an established connection, followed by re-establishing it based on the correct sequence and acknowledgement numbers with the attack host machine.
How to Prevent IP Spoofing?
Organizations can adopt measures to stop spoofed packets from infiltrating their networks, including:
- Using a network attack blocker.
- Using strong verification methods for all remote access, including for systems on the enterprise intranet in order to prevent accepting spoofed packets from an attacker who has already breached another system on the enterprise network.
- Authenticating IP addresses of inbound IP packets.
- Monitoring networks for atypical activity.
- Deploying packet filtering systems that can detect discrepancies, such as outgoing packets with source IP addresses that do not match those on the company's network.
Firewalls play a crucial part in blocking IP packets with spoofed addresses, and it is essential for all enterprise routers to be configured with the ability to reject packets with spoofed addresses. Some of the basic considerations include:
- Blocking traffic that develops from within the enterprise but that spoofs an external address as the source IP address; this avoids spoofing attacks from being initiated from within the enterprise against other external networks.
- Configuring firewalls and routers to reject packets with private IP addresses that originate from outside the enterprise perimeter.
IP Address Spoofing Prevention
Protecting your IP address is thus an essential feature that will protect your own identity. This security can be enhanced by installing a reliable and good web security tool that is incorporated with an efficient web application firewall (WAF) and several other noteworthy security features capable of preventing DoS and DDoS attacks. cWatch Web is one reliable web security software that has been developed by Comodo. This Managed Security Service for websites and web applications has an excellent WAF capable of eliminating application vulnerabilities and protecting web applications and websites against advanced attacks such DDoS, Cross-Site Scripting and SQL Injection. Available with malware scanning, vulnerability scanning, and automatic virtual patching and hardening engines, the Comodo WAF has the potential to provide robust security that is wholly managed for customers as part of the Comodo cWatch Web solution.
Key Benefits of the Comodo WAF
Following are some of the key security benefits offered by the Comodo WAF:
- Malicious Bot and Brute Force Prevention: Malicious bots and brute force attacks are blocked from websites. Protection is also provided for account registration forms and login pages from different attack vectors including protection from application denial of service, web scraping, and reconnaissance attacks.
- Zero Day Immediate Response: Regular updates of virtual patches for all websites under management and instant response to applying a patch for the zero day attacks when they become known to the public.
- Stop Website Attacks and Hacks: Protects vulnerable websites by detecting and removing malicious requests and preventing hack attempts. This WAF also focuses on application targeting attacks, for example, WordPress and plugins, Drupal, Joomla etc.
- DDoS Protection: Globally-distributed Anycast network allows efficient distribution of traffic. It explicitly blocks all nonHTTP/HTTPS-based traffic, with a current network capacity in excess of 1 TB/s. Each PoP has multiple 10G and 100G ports, designed to scale and absorb extremely huge attacks.
Other Web Security Features Offered by Comodo cWatch Include:
- Secure Content Delivery Network (CDN): A global system of distributed servers to improve the performance of web applications and websites.
- PCI Scanning: Enables service providers and merchants to stay in compliance with the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS).
- Malware Monitoring and Remediation: Detects malware, provides the methods and tools to remove it and prevents future malware attacks.
- Cyber Security Operations Center (CSOC): A team of certified cybersecurity professionals providing round-the-clock surveillance and remediation services.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): Enhanced intelligence that can leverage existing events and data from more than 85M endpoints and 100M domains.





