DDoS Meaning - What is a Distributed Denial of Service Attack?
Distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) refers to a computer attack that uses several hosts to overpower a server, causing a website to crash. Hackers execute DDoS attacks to permanently or temporarily disable large-scale, popular sites. Often, this is carried out by attacking the targeted server with a high volume of information requests, which overloads the main system and inhibits it from working, which then prevents the website's legitimate users from accessing the site.
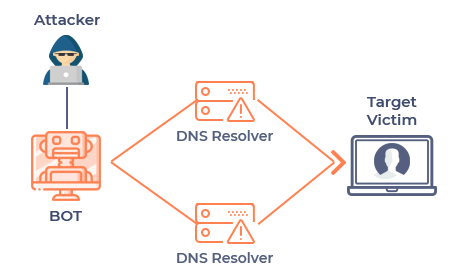
DDoS attacks can be designed to target any aspect of a business and its resources by:
-
Crashing the operating system
-
Targeting alarms, printers, laptops, or phones
-
Disabling a particular computer, service, or an entire network
-
Hitting system resources like disk space, bandwidth, processor time, or routing information
-
Exploiting operating system vulnerabilities to drain system resources
-
Executing malware that affects processors and activates errors in computer microcode
Even though DDoS is less complicated than other forms of cyberattacks, this mode continues to grow stronger and more sophisticated. There are three basic categories of attack:
-
TCP State-Exhaustion Attacks
These attacks focus on web servers, load balancers, and firewalls, exhausting the finite number of concurrent connections the device is capable of supporting. -
Application Layer Attacks (connection-based)
Also known as "Layer 7 attacks," application layer attacks target weaknesses in a server or application to establish a connection and exhaust it by monopolizing transactions and processes. These refined threats are very difficult to detect because not many machines are needed for the attack, yielding a low traffic rate that can appear "normal." -
Volumetric Attacks (connectionless)
Also known as "floods," these attacks aim to send so much traffic that it overpowers the bandwidth of the site. Volumetric attacks are mostly executed using botnets, which are armies of computers infected with malicious software and controlled as a group by the hacker.
DDoS attackers are primarily motivated by:
-
Ideology: "Hacktivists" use DDoS attacks to target websites they disagree with ideologically.
-
Extortion: Perpetrators use DDoS attacks, or even just the threat of DDoS attacks, as a means of taking money from their targets.
-
Cyberwarfare: Government-authorized DDoS attacks are employed to cripple opposition websites or an enemy country's infrastructure.
-
Business feuds: Businesses use DDoS attacks to strategically take down competitor websites.
-
Boredom: Cyber vandals (or script-kiddies) use prewritten scripts to launch DDoS attacks. The perpetrators of such attacks are typically bored hackers who are seeking an adrenaline rush.
DDoS Attacks: Defense and Prevention
DDoS attacks can lead to major business risks with lasting effects. It is important for IT and security managers and administrators, as well as business executives, to understand the vulnerabilities, threats, and risks associated with DDoS attacks.
The business impact of DDoS attacks can be reduced by adopting some key information security practices, including performing ongoing security assessments to look for and resolve a denial of service-related vulnerabilities, as well as using security controls such as services from cloud-based vendors who specialize in responding to DDoS attacks.
Solid patch management practices, user awareness, and email phishing testing, including proactive network monitoring and alerting, can help decrease an organization's contribution to DDoS attacks across the internet.
Comodo Cybersecurity developed cWatch as an all-in-one web security tool that is capable of preventing DDoS attacks. The cWatch Web Application Firewall eliminates application vulnerabilities and protects websites and web applications against advanced attacks including but not limited to DDoS, cross-site scripting, and SQL injection.
Other web security features offered by Comodo cWatch:
- Secure Content Delivery Network (CDN): A global system of distributed servers to enhance the performance of web applications and websites.
- Cyber Security Operations Center (CSOC): A team of always-on certified cybersecurity professionals providing round-the-clock surveillance and remediation services.
- Malware Monitoring and Remediation: Detects malware, provides the methods and tools to remove it and prevents future malware attacks.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): Advanced intelligence that can leverage existing events and data from 85M+ endpoints and 100M+ domains.
- PCI Scanning: Enables service providers and merchants to stay in compliance with the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS).
- Web Application Firewall (WAF): Powerful, real-time edge protection for web applications and websites, providing enhanced filtering, security and intrusion protection.
To know more about DDoS Meaning contact our technical experts and get The DDoS Attack Definition guide quickly!
Related Resources





