Types of Website Threats
Website threats come in various forms, each posing a unique risk to the security and integrity of a website. Understanding these threats is crucial for implementing effective security measures. Here are some common types of website threats:
- Malware: Malware, short for malicious software, includes viruses, worms, Trojans, and spyware. It can be used to steal sensitive information, disrupt website operations, or gain unauthorized access to a server.
- Phishing: Phishing attacks involve deceiving individuals into providing sensitive information like login credentials or credit card numbers. These attacks often occur through fraudulent emails or websites that mimic legitimate ones.
- SQL Injection: This occurs when an attacker uses a web form field or URL parameter to manipulate or exploit a website's database. If successful, it can result in unauthorized viewing or manipulation of database information.
- Cross-Site Scripting (XSS): XSS attacks occur when attackers inject malicious scripts into content from otherwise reliable websites. These scripts can then execute on the user's device, potentially leading to data theft or manipulation.
- Denial of Service (DoS) and Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS): DoS and DDoS attacks overwhelm a website's resources, making it inaccessible to legitimate users. DDoS attacks are more potent as they originate from multiple sources.
- Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF): CSRF tricks a user's browser into executing unwanted actions on a website where the user is authenticated. It can lead to unauthorized changes or data theft.
- Brute Force Attacks: These attacks involve attempting numerous login combinations to gain unauthorized access. They exploit weak passwords and can lead to unauthorized access to sensitive areas of a website.
- Zero-Day Exploits: These attacks target software vulnerabilities before the developer has released a fix or even before the vulnerability is known.
- Session Hijacking and Man-in-the-Middle Attacks: These attacks intercept a user's and a website's communication to steal or manipulate data.
- Comment Spam: This involves posting unwanted or irrelevant comments, usually for promotional purposes, which can harm a website's credibility and SEO ranking.
Each of these threats requires specific strategies and tools to mitigate. For instance, firewalls and antivirus software can help combat malware, while strong, regularly updated passwords and two-factor authentication can reduce the risk of brute-force attacks. Regular security audits and staying informed about new threats are also vital to maintaining robust website security.
Best Practices for Website Security
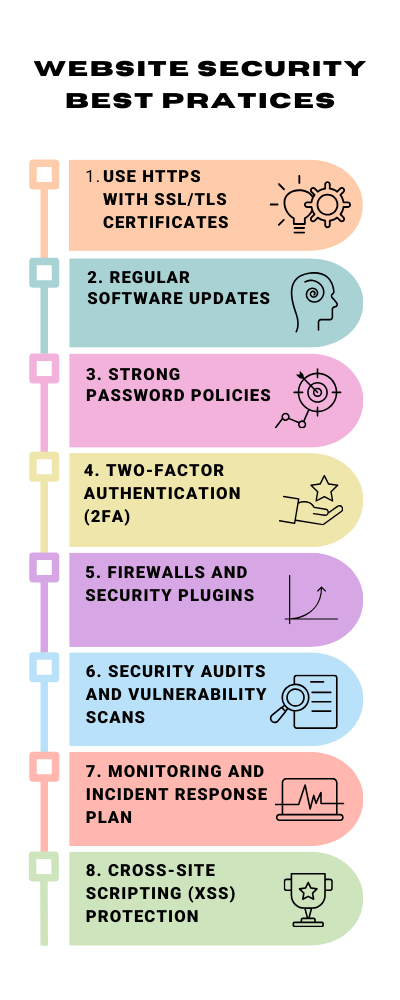
Implementing best practices for website security is essential to protect against cyber threats. Here are key strategies to enhance the security of a website:
- Use HTTPS with SSL/TLS Certificates: Encrypting data transferred between the user and the server is crucial. Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) or Transport Layer Security (TLS) certificates enable HTTPS on your site, ensuring data integrity and confidentiality.
- Regular Software Updates: Keep all website software, including the content management system (CMS), plugins, and scripts, updated. Many attacks target vulnerabilities in outdated software.
- Strong Password Policies: Enforce solid and unique passwords for all user accounts, especially for admin-level access. Consider implementing password complexity requirements and regular password change policies.
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Adding an extra layer of security with 2FA can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access. 2FA requires a second verification form, such as a text message code, an authentication app, and a password.
- Firewalls and Security Plugins: Use web application firewalls (WAF) to monitor and filter incoming traffic to your site. Security plugins can also provide additional defenses against common threats.
- Regular Backups: Regularly back up your website data and ensure that these backups are stored securely. This enables you to restore your website quickly in case of a cyberattack or data loss.
- Security Audits and Vulnerability Scans: Conduct regular security audits and vulnerability scans to identify and address potential security weaknesses in your website.
- Limit User Access: Practice the principle of least privilege by limiting user access to only what is necessary for their role. This minimizes the risk in case of a compromised account.
- Educate Users and Staff: Train users and staff on security best practices, including recognizing phishing attempts and safely handling sensitive data. Monitoring and Incident Response Plan: Continuously monitor your website for suspicious activity and have an incident response plan. Quick response to a security breach can significantly reduce the impact.
- Secure File Uploads: If your website allows file uploads, ensure these files are scanned for malware and stored securely to prevent exploits. Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) Protection: Implement measures to prevent XSS attacks, such as content security policies and sanitizing user input.
By applying these best practices, you can significantly enhance the security of your website, protect sensitive data, and maintain the trust of your users and customers. Website security is an ongoing process requiring constant vigilance and adaptation to emerging threats.
Why Choose cWatch for Website Security?
Choosing cWatch for website security offers numerous benefits, making it popular for businesses and website owners looking to protect their online presence. Here's why cWatch is a preferred option for website security:
- Comprehensive Security Suite: cWatch provides an all-in-one security solution, including malware detection and removal, firewall protection, DDoS mitigation, and vulnerability scanning. This comprehensive approach ensures multiple layers of security.
- Real-Time Monitoring and Threat Detection: cWatch offers real-time monitoring, which is crucial for detecting and responding to threats as they occur. Its advanced threat detection capabilities can identify even the most sophisticated attacks.
- 24/7 Expert Support: One of cWatch's standout features is its round-the-clock expert support. Users have access to a team of security professionals who can assist with any security concerns or incidents.
- Proactive Malware Removal: cWatch detects malware and actively removes it. This proactive approach ensures that threats are not just identified but are also dealt with promptly.
- DDoS Protection: Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks can cripple a website. cWatch offers robust DDoS protection to keep your website accessible and operational even under attack.
- SSL Support: cWatch supports SSL/TLS encryption, which is critical for website security and data privacy. It ensures that the data transferred between the user and the server is encrypted and secure.
- Customizable Security Policies: cWatch allows users to customize security policies based on their needs. This flexibility ensures that the security measures are aligned with the unique requirements of each website.
- Easy Integration: cWatch is designed for easy integration with many websites and platforms. This ease of integration means businesses can implement cWatch without extensive technical expertise.
- Compliance and Risk Management: For businesses needing to comply with various regulations like GDPR or PCI DSS, cWatch helps manage these compliance requirements, reducing the risk of legal and financial penalties.
- Affordability: Despite offering a comprehensive suite of security features, cWatch is known for its affordability, making it an accessible option for businesses of all sizes.
In conclusion, cWatch stands out due to its comprehensive security offerings, expert support, proactive threat management, and ease of use. Its ability to provide a robust defense against a wide range of cyber threats, combined with affordability and compliance support, makes it an excellent choice for enhancing website security.
Website Security FAQ
Answer: Website security refers to the measures and protocols to protect a website from cyber threats such as hacking, malware, and data breaches. It involves various strategies and tools to safeguard a website's content, protect user data, and ensure uninterrupted service. Essential practices include using SSL/TLS certificates, regularly updating software, enforcing strong password policies, and employing firewalls and antivirus programs.
Answer: Website security is crucial for protecting sensitive data, maintaining user trust, and ensuring the smooth operation of online services. A lack of security can lead to data theft, customer trust loss, reputation damage, and potential legal consequences. Search engines also favor secure websites, impacting a site's visibility and SEO ranking. Additionally, robust security helps comply with data protection regulations and standards.
Answer: Ensure all software and plugins are current to enhance your website's security. Use strong, unique passwords and consider implementing two-factor authentication for added protection. Employ a web application firewall (WAF) to monitor traffic and block malicious activities. Regularly back up your website and use SSL/TLS certificates for secure data transmission. Additionally, educate your team about security best practices and the latest security threats and trends.






